Why is Styrofoam a Good Insulator for Heat? Unveiling the Science!
The Remarkable Science and Practical Applications of Styrofoam's Heat Insulation

© by pexels.com
✓ Last Updated: November 15, 2023
If you've ever sipped a hot coffee from a Styrofoam cup without burning your fingers, you might have wondered: why is Styrofoam such an effective heat insulator? Beyond its role as a ubiquitous packaging material, Styrofoam, technically known as expanded polystyrene (EPS), boasts impressive thermal insulation capabilities. Let's dive into the science of why Styrofoam is an exceptional heat insulator and its practical applications.
© by pexels.com
The Secret Behind Styrofoam's Insulating Power
Styrofoam's heat insulation prowess can be attributed to its structure. It consists of 95% air, trapped within a matrix of interconnected polystyrene beads. This air acts as an insulator, slowing down the transfer of heat. The key factors contributing to Styrofoam's effectiveness as a heat insulator are:
- 1 - Air Pockets: Styrofoam is comprised mainly of air pockets. Air is a poor conductor of heat, and these pockets act as barriers that prevent the transfer of thermal energy.
- 2 - Low Thermal Conductivity: Polystyrene, the material of which Styrofoam is made, has low thermal conductivity. This means it resists the flow of heat.
- 3 - Closed-Cell Structure: Styrofoam is a closed-cell foam, which means its cells are sealed off from each other. This minimizes heat transfer through convection.

© by freepik.com
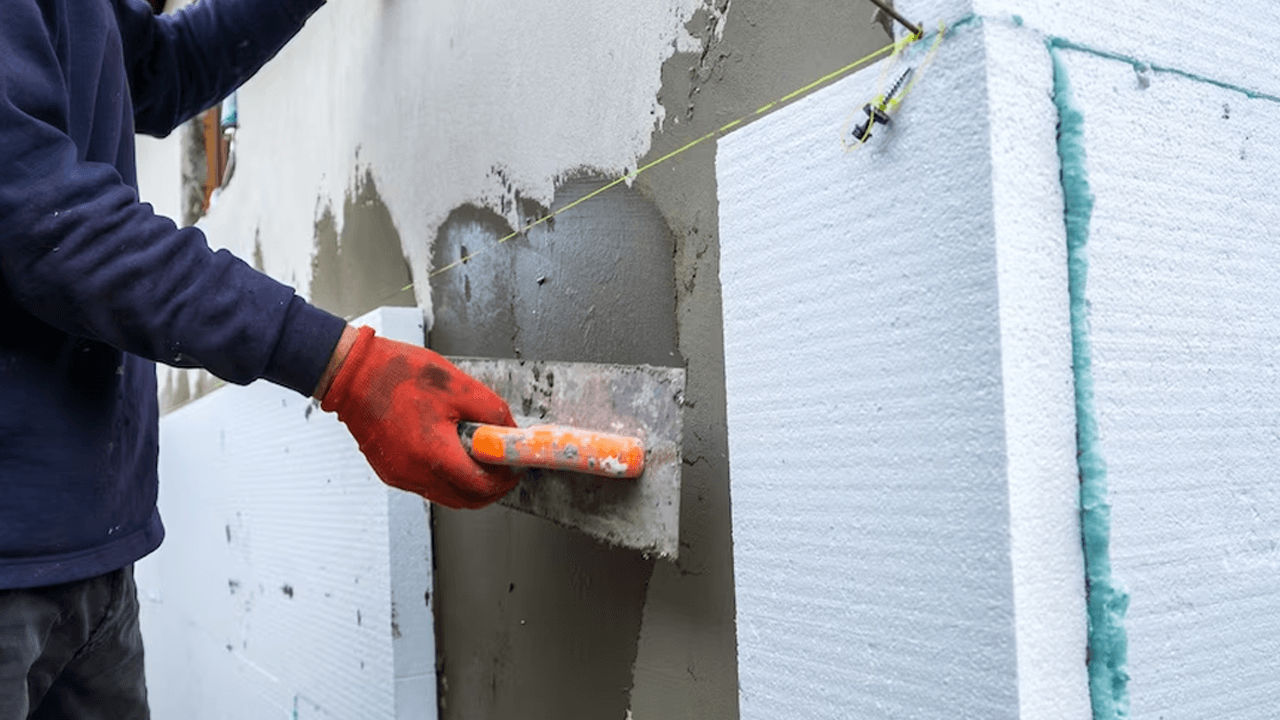
Practical Applications of Styrofoam Insulation
Styrofoam's impressive heat insulation properties make it an excellent choice for a variety of applications, including:
- 1 - Building Insulation: Styrofoam boards are used to insulate walls, roofs, and floors in homes and commercial buildings. They help maintain a comfortable indoor temperature and reduce energy consumption.
- 2 - Packaging: Its lightweight nature and heat insulation capabilities make Styrofoam an ideal choice for shipping delicate items that require temperature control.
- 3 - Cups and Containers: Styrofoam cups and food containers keep hot beverages hot and cold beverages cold. They're also easy to hold without getting too hot on the outside.
- 4 - DIY Projects: Styrofoam sheets and blocks are popular for DIY craft projects and model building, showcasing its versatility beyond the industrial and commercial realms.

© by styrofoamworld.com
In conclusion
the science behind Styrofoam's effectiveness as a heat insulator is rooted in its air-filled, closed-cell structure and low thermal conductivity. Its practical applications range from maintaining building temperatures to preserving the warmth of your morning coffee. So, the next time you enjoy a hot drink in a Styrofoam cup, you'll appreciate the impressive science behind its heat-insulating magic! Cheers to staying warm (or cool) with Styrofoam!




